The aggressive incentive policies that China has carried out in the last decade in the battery sector, and electric car sector, has taken it from irrelevance to a first world position. A domain that the United States and Europe are now trying to counteract with large investments that will allow them to climb places.
According to Bloomberg’s data, in 2020, China has surpassed Japan and South Korea, which had been the leaders until then. A situation caused mainly by the tremendous domestic demand from local manufacturers and Western manufacturers settled in the Chinese market, leading them to accumulate a production of 72GWh.
Another key factor is with the addition to volume, China also controls a good part of the components that make up these batteries, with 80% of the refining of raw materials worldwide, 77% of the production capacity of cells, and 60% of battery-related component manufacturing.
Control of the supply chain of raw materials gives China a dominant position and significant influence even over manufacturers outside its borders.
Now Europe and the United States are trying to cope with this avalanche. In the coming years, both blocks will try to create their battery production centers that will challenge the Asian giants in this burgeoning sector. A dynamic in which, according to Bloomberg, Europe is progressing favorably, but the United States is lagging behind.
The Bloomberg ranking of lithium battery producers allows us to see how the current situation is and how it will evolve between 2020 and 2025. A study classifies countries in five critical issues related to the supply chain: raw materials, manufacturing of cells and components, environment, regulations, infrastructure and innovation, and final demand both in electric cars and in stationary storage.
As we see in the Bloomberg graph, in 2020, China is the clear dominator of the ranking in all areas, except for the environment and regulations, infrastructure, and innovation. Aspects that in the case of the environment, as we see five years later, have drastically improved, ranking first in this regard.
A list that supposes a projection on which there may be variables at stake, such as the results of the elections in the United States, where a victory for Democrat Biden could boost investments in renewable energy, electric cars, and batteries.
Factors such as Brexit will also come into play, which could negatively affect the United Kingdom with an estimated 152 GWh production per year for 2025, which it needs to place in continental Europe since it supposes a capacity multiplies its internal demand by five. Something that will be more difficult in a no-deal Brexit.
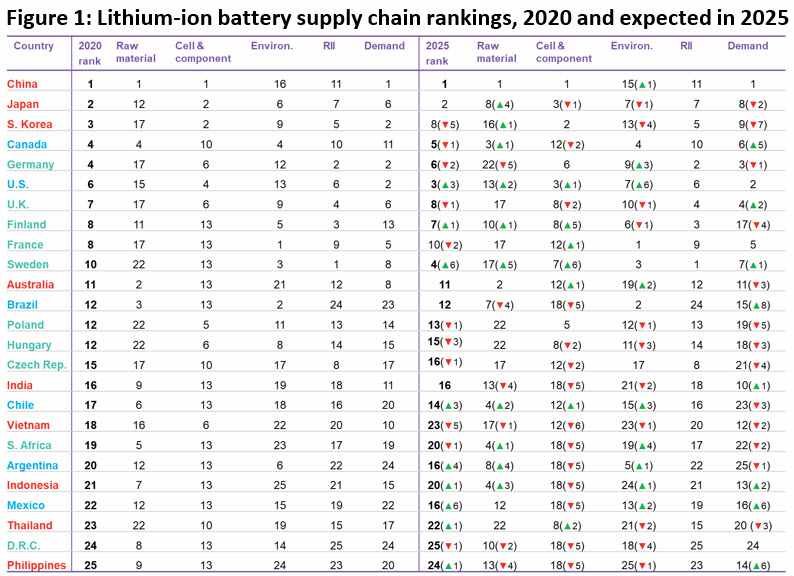
Overall ranking in 2025
1. China
2. Japan
3. United States
4. Sweden
5. Canada
6. Germany
7. Finland
8. The UK
9. South Korea
10. France