Read The Full Article On: Caranddrive
We explain EPA ratings, factors that affect range, how EVs have performed in our testing, and why it’s all very complicated.
When it comes to electric vehicles, range is the all-important stat. Whether or not you make it to the next public-charging spot, are able to complete your daily commute, or are instead stranded on the side of the road depends on it.
Range is so heavily scrutinized because EVs can travel average barely half the distance of gas-powered vehicles before they require a “fill-up” and because gas pumps are far more ubiquitous than fast chargers. Most EV range discussions are centered around the EPA combined range, as that’s the one that’s published prominently on the window sticker. For the 2020 model year, 33 EVs have EPA ratings (this includes multiple variants of the same vehicle), and the combined-range figures span from 110 miles for the Mini Cooper Electric to 373 miles for the Tesla Model S Long Range.
There’s More than One EPA Range Figure
As with gas vehicles’ EPA fuel-economy estimates, there are also separate ratings for EVs’ city and highway range, too. Unlike gas-powered vehicles, whose highway efficiency almost always exceeds the city figure, all EVs except the Porsche Taycanhave higher city range ratings than highway. Part of electric vehicles’ magic in low- and variable-speed scenarios is their ability to recapture energy when decelerating by slowing the vehicle using the electric motor (or motors) rather than the traditional brakes.
Another way EVs are different is that range and efficiency aren’t directly related. That’s because of charging losses; roughly 85 to 90 percent of the total energy that comes from the wall makes it into the battery pack. That’s why there are two terms used: efficiency, which can be expressed in MPGe, includes charging losses, while consumption, the energy use while driving, doesn’t include them.
Our EV range test is done at a steady 75 mph, because highway driving is where range matters most. If you’re looking to cover 500 or 1000 miles in a day, it necessarily has to be done at high speeds. There’s just not enough hours in the day to do otherwise. Even the shortest-range EV can manage more than 7 hours of slogging through city traffic at an average speed of, say, 15 mph. Also, unlike a gas-powered vehicle, an EV’s consumption increases dramatically as speeds rise. Of course, as with all cars, aerodynamic drag inflates with the square of speed, but EVs are particularly affected as all but the Porsche Taycan lack multiple gears. So, a higher vehicle speed means the electric motor is spinning at a faster and less-efficient point.
No EV Has Yet to Match or Exceed Its Range Rating in Our 75-MPH Highway Test
Unlike gas- or diesel-powered vehicles, which regularly beat their EPA ratings in our highway testing, every one of the 12 EVs that we’ve run range tests on to date has fallen short of both its EPA highway and combined figures. We use the combined figure as the primary point of comparison because the city and highway range figures for EVs are much closer than for gas-powered vehicles, and we want to avoid confusion by using something other than that most-familiar figure.
The closest result was achieved by a 2019 Audi e-tron, which chalked up 190 miles, or 93 percent of its combined rating, while the worst was a 2019 Hyundai Kona Electric, whose 160-mile result is only 62 percent of its rating.
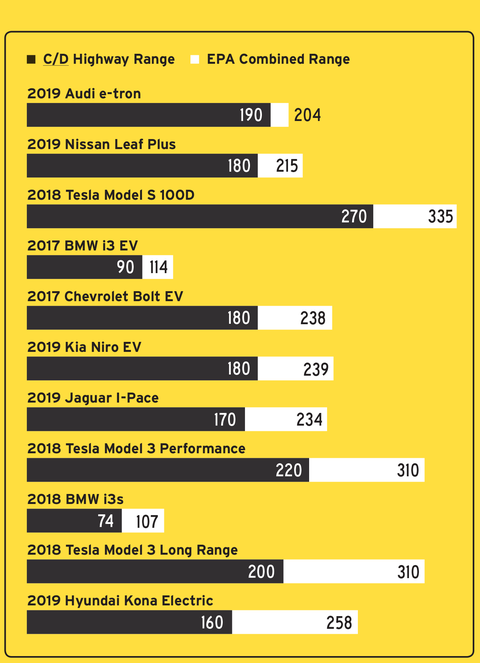
ALL THE EVS WE’VE TESTED, ARRANGED BY HOW CLOSE THEY CAME TO THEIR EPA RANGE RATING IN THE REAL WORLD. CAR AND DRIVER
We don’t (yet) control the weather, so the worst-performing examples, including a 2018 Model 3 that only managed 65 percent of its range rating, took place with outside temperatures hovering around freezing. Which brings up another way EVs are different: cold weather affects range dramatically. One of the many reasons for that is that using the heater to warm the cabin—particularly on EVs that have resistive heaters—sucks a lot of juice. In a test with our long-term Model 3 we found that using the heat can increase consumption by as much as 35 percent and kill 60 miles of range, a significant chunk of the Model 3’s 310-mile EPA rating.MORE ON EV RANGEHow Much Does Climate Control Affect EV Range?How Cold Weather Affects EV RangeRange Anxiety in Death Valley in a Chevy Bolt
Also, you should consider our range figures the absolute maximum possible and, as with our 0-to-60-mph times, it will be difficult to achieve them with any regularity. That’s because it involves charging the battery all the way to 100 percent, which is not the EV norm. Topping off the last 10–15 percent is when the rate of charging slows considerably, and it also leads to increased degradation in battery capacity over time. For example, Tesla recommends limiting charging to 90 percent for daily use. Even on long-distance trips, the stops are determined more by the charging infrastructure than anything else, and the most expeditious method is to top up the battery just far enough—to maybe 80 or 90 percent, keeping it in the speedy part of the charge-rate curve—to get to the next charger.
Range is critical, range is complicated. And if you want to drive an EV long distances and you live in a place where it gets cold, plan on a large buffer between the EPA combined rating and what you actually will be able to use.

